业务场景
对之前已有的试用用户申请规则进行拓展。
1 | if (是否海外用户) { |
分析:
- 主要流程主要是基于 and 或者 or 的关系。
- 如果有一个不匹配,后续的流程不用执行,需要具备一个短路的功能。
- 如果在原有基础上改,稍微注意解决需求不是大问题,但后面可维护性非常差。
规则执行器设计
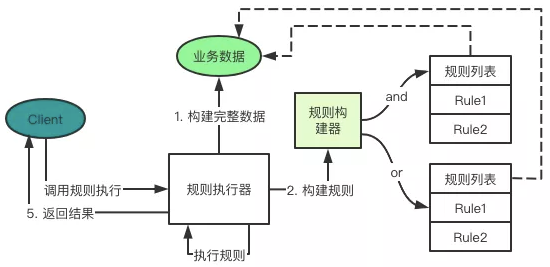
对规则抽象
1 | // 业务数据 |
规则实现
1 | // 具体规则- 例子1 |
执行器构建
1 | public class RuleService { |
执行器调用
1 | public class RuleServiceTest { |